



I will sharing my information and experience about the cancer treatment in Lahore. I will also be writing my opinion about the Cancer hospitals and oncologists based on my experience in Lahore. I will be sharing my personal opinion (how they treated me) you can disagree but my criticism should be taken as constructive.
Options Available For Cancer Diagnostics and Treatment in Lahore :
Use of Mobile Communication Technology and Information Flow for Crop Yield and ROI Optimization
Pakistan’s high potential for producing food is an internationally established fact. However, agriculture sector in Pakistan is facing significant challenges. Some of these challenges are:
i. Shortage of water and power.
ii. Rising cost of inputs.
iii. Extremely high post harvest wastage of farm produce.
Fortunately, progress in mobile communication and information technology has the potential to provide significant support to farmers in surmounting these challenges. Some of the technologies that can be leveraged include:
i. Mobile communication and smart consumer devices like phones, pdas etc.
ii. Internet and cloud computing.
iii. Cost effective satellite imaging and image processing.
iv. Plant growth modeling and simulation.
v. Knowledge synthesis and data mining.
Integrated use of these technologies can lead to optimization of individual farmer’s operations as well as accurate estimation of total farm production at a fine grain spatial as well as temporal resolution. These fine grain estimates can be used to minimize waste by optimizing use of current supply chain infrastructure as well as accurately identifying gaps in this infrastructure.
A number of efforts have been made to leverage mobile communication to assist farmers. These efforts have had mixed results. A detailed literature search on this topic is beyond the scope of this document. One of the key short comings in these efforts has been a lack of analysis and understanding of farmers’ end-to-end information flow requirements. This document describes farmers’ information flow needs for optimizing crop yield and ROI. Major steps in farming, farmer’s information needs for each step, sources of information, challenges and bottlenecks in receiving information and technologies for addressing these challenges are described.
A farmer takes following eight major steps from crop selection to harvesting:
i. Crop Selection
ii. Land Preparation
iii. Seed Selection
iv. Seed Sowing
v. Irrigation
vi. Crop Growth
vii. Fertilizing
viii. Harvesting
Farmers typically rely on following sources of information:
i. Agriculture department of provincial government.
ii. Fellow farmers.
iii. Field agents of seed, pesticide and fertilizer companies.
iv. TV and radio programs.
v. Newspapers.
Farmers typically face following challenges in receiving timely and personalized information:
i. Farmer has to travel to offices of agricultural department for information. This is a costly and time consuming activity. Availability of government officials is unpredictable.
ii. Radio or TV programs are broadcast at a predefined schedule which may or may not be convenient for the farmer. Information should be available to the farmer on demand and should be personalized to his needs. Majority of farmers in villages either do not have access to newspapers or lack of education makes their access limited.
iii. Most of the information broadcast may not be specific to a farmer’s needs.
iv. Fellow farmers don’t have best or most up to date knowledge.
v. Field agents of pesticide or seed companies are unable to pay frequent and timely visits to all farmers.
A number of information flow problems can be resolved by leveraging information technology to maintain comprehensive personalized knowledge about a farmer’s operations, simulation and modeling tools and two way asynchronous communications between farmers and the IT system using mobile communication technologies.
Cost of these technologies has decreased beyond expectation. Pakistan has one of the least expensive mobile communication networks in the world. Reasonably priced intelligent mobile devices are capable of taking good quality images and sending these to experts for diagnosis. Large scale computation for decision making is available all over the world at very affordable prices. Plant growth modeling and simulation technology is maturing.
Farmers’ information needs for each of these steps are presented next.
Pakistan’s agriculture sector is ripe for leveraging information technology and mobile communication to optimize crop yield and ROI. Fortunately, several advances in technology have taken place internationally as well as in Pakistan. Key challenge we face is to develop comprehensive understanding of farmers’ information flow needs and develop integrated solutions that provide information to farmers, when and where needed, at their convenience. Success of this initiative strongly depends upon receiving accurate and timely information from farmers. The IT system should be capable of efficient information flow management, knowledge synthesis and information delivery to the farmer. This will be possible only if farmers perceive value in information this system provides them.
A very useful article
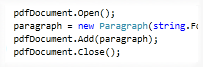 This post illustrates how you can dynamically create a number of PDFs on the fly, zip them all up, and return the ZIP file via a HTTP response.
This post illustrates how you can dynamically create a number of PDFs on the fly, zip them all up, and return the ZIP file via a HTTP response.
I’ve created a sample project which you can download that has a working example of the source code referenced in the post – ZippingPDFs.zip (1.5 MB). For simplicity I went for an ASP.NET web application. The only requirements are that you have Visual Studio 2010 installed.
View original post 619 more words
For high availability of data in your SQL server, you might require a replica of your database server. To server this purpose you can use MS SQL Server’s mirroring functionality. By using the mirroring feature we can create a replica of our database being synchronized real-time. Your same data will be saved at two different servers. In MS SQL Server Mirroring there are three different modules i.e.
Practically all three servers are on different machines. Principal is the server whose database replica will be being synchronized at the Mirroring Server. Witness server performs the failover duties, incase principal server goes down Witness Server will perform automatic failover to make mirroring as principal server. Supporting automatic failover is the only role of the witness.
Now how to install database mirroring in MS SQL Server?
Take the back up of desired database (which needs to replicated/mirrored) on the Principal SQL Server.
Create a database with the same name from the Principal SQL Server on the Mirroring SQL Server, then restore the backup on the Mirroring SQL Server with the
Option to Overwrite the existing database checked
RESTORE WITH NORECOVERY Option
After you click “OK” button, you will see it’s in a Restoring mode as you have chosen the NORECOVERY option and it will be in a permanent Restoring state to prevent users from accessing the database. It will be only user accessible if the database fails over to the Mirror and now the old Principal will go to the recovering state.
Start the mirroring configuration process on the Principal SQL Server. Right-click the Database –> Properties –> Mirroring and click Configure Security.
On the Include Witness Server screen, select “Yes” and click “Next” Button.
Now choose Principal SQL Server Instance:
Now choose Mirror SQL Server Instance:
Choose a Witness Instance:
Now enter the SQL Server Service Accounts for each SQL Server Instance, but if all of your SQL instances are using the same account, then just leave it blank.
Completing the Wizard:
Start the mirroring:
Credits: I have learnt Mirroring from Code Project, I have also taken some images from that article. So I am full credit to , the Arthur of Article at Code Project.
Use of .NET BackGroundWorker
One of the most important things that differentiates a “quick and dirty” application from one that has been designed well is how the application’s user interface behaves during lengthy operations. The quick-and-dirty approach is to just do all of your work in a button’s Click event handler and not worry about the user interface. The problem with this is that the GUI will freeze up while the application does whatever work it needs to do.
A well designed application, on the other hand, is one that is careful to do as much work as possible in background threads, keeping the GUI responsive and making sure that it makes it obvious to the user that work is going on in the background and adjusts the GUI to disallow any user actions that don’t apply until after the work finishes.
Under .NET 2.0, doing work on a background thread has become a…
View original post 2,714 more words
Private Function TargetValue()
Dim valueRet As String
Dim srv As Server
Dim dt As New PITimeFormat
Dim pt As PIPoint
Dim MYPIServer As PISDK.Servers
Set srv = PISDK.Servers.DefaultServer
TargetValue = srv.PIPoints(“Target”).Data.Snapshot
‘ Target is the tag name here.
End Function
‘***************************Writing into Target Tag****************************
Private Sub WriteTargetInstructionPI()
Dim srv As Server
Dim dt As New PITimeFormat
Dim pt As PIPoint
Dim MYPIServer As PISDK.Servers
Set srv = PISDK.Servers.DefaultServer
TagName = “Target”
Set pt = srv.PIPoints(TagName) ‘ it’s your PI point
dt.InputString = “*” ‘it’s data. InputString – Converting String in PIdata format
pt.Data.UpdateValue TextBoxTarget.Text, dt, dmReplaceDuplicates ‘function for Update (reed help)
End Sub
Note: I have used Sub for writing the tag value and Function for reading tag value for my own business logic. You can use either Function or Sub according to your own requirements.
Inductive Automation uses OPC UA to build its industrial platform on Java and offers the Ignition OPC UA server for free, whether users purchase the Ignition software or not. Keep reading to request a free activation key.

In order to achieve their goals of a software platform that would work on any system, Inductive Automation needed an OPC server that wouldn’t lock their software into a Windows-only environment.
“We made the decision that we wanted everything written in Java so that users would have the freedom to choose their operating system,” said Colby Clegg, software developer for Inductive Automation. “The platform-neutral OPC UA specification enabled us to write our own stack in Java. Now our entire software package is in Java, and this offers a lot of benefits for users.”
The result was the Ignition OPC UA server, which can work either as a stand-alone OPC server for third-party OPC UA clients, or as part of the comprehensive Ignition software package. In either case, it provides fast, reliable, and secure access to PLC data through its pluggable driver architecture.
Why Java?
Java is one of the most popular programming languages in the world (see the TIOBE Programming Community Index for September 2010). Java runs on more types of consumer and embedded devices, smart cards, ATMs, thin clients, PCs, servers, and mainframes than any other language.
“Java is the ‘write once, run anywhere’ language,” said Steve Hechtman, president of Inductive Automation. “This is a major reason why we selected it. By writing Ignition in Java, it runs equally well on Linux as it does on OSX, Windows or Solaris.”
Java is also highly resistant to viruses. It is designed from the ground up to be more secure than legacy programming languages, offering a rich array of features that prevent many common security holes. That makes it ideally suited to the industrial environment.
“Rather than following the flock and just selecting the current Microsoft technology, we took a step back and evaluated what language provided the most portability, security, stability and support—and Java was the clear winner,” Hechtman said.
Why Free?
Inductive Automation offers the Ignition OPC UA server for free, whether users purchase the Ignition software or not. “We want the market to get excited about the potential of OPC-UA,” explains Clegg, “and in the freedom of selecting your own platform. Plus, once users get started with Ignition, we’re confident that they’ll be blown away by everything it can do.”
The Ignition OPC-UA server is free and can be used with any OPC-UA client: Simply request a free activation key, download the software, and get started using it on your control system. It features an open driver API, and includes free Allen Bradley and Modbus TCP drivers.
The activation key and download page can be accessed here:https://www.inductiveautomation.com/products/ignitionopc/download
This article is fully copied from
http://www.automationworld.com/opc-ua-stack-written-java-write-once-run-anywhere
All credit goes to it’s parent website. I have just shared this information
Dim Req As New XMLHTTP
Dim Resp As New DOMDocument
Dim Weather As IXMLDOMNode
Dim CurrentWeather As IXMLDOMNode
Req.Open “GET”, “http://api.worldweatheronline.com/free/v1/weather.ashx?q=Karachi&format=xml&num_of_days=1&key=enter_you_own_key_by-registering”, False
Req.Send
Resp.loadXML (Req.responseText)
For Each CurrentWeather In Resp.getElementsByTagName(“current_condition”)
Me.LabelTemp.Caption = ” ” & CurrentWeather.SelectNodes(“temp_C”)(0).Text
Me.LabelTemp1.Caption = ” ” & CurrentWeather.SelectNodes(“humidity”)(0).Text
Me.LabelTemp2.Caption = ” ” & CurrentWeather.SelectNodes(“windspeedKmph”)(0).Text
Me.LabelTemp4.Caption = ” ” & CurrentWeather.SelectNodes(“winddir16Point”)(0).Text
Me.LabelTemp3.Caption = ” ” & CurrentWeather.SelectNodes(“pressure”)(0).Text
Next
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 (Standard Edition) Installation Guide
This document will guide you step by step installation of Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 Standard Edition on Window Server 2008 R2.
Open the installation media, you will see the list of files. Run “Setup.exe” as show below.
Figure 1: Setup.exe
On running the “setup.exe” following screen will appear.
Click “Installation” from the top of left side of window. Select “New installation add features to an existing installation” at top of right side of window. See the figure below.
Following screen will appear for some time
Following screen will appear, press “OK” button.
Figure 2: Setup Support Rules
In this step you will enter registration key of MS SQL Server 2008 R2. After entering registration key successfully press “Next” button. See the figure below.
Figure 3: Product Registration Key
This step will ask you to accept the license terms and condition. Check the both check boxes and press “Next” button. See the figure below.
Figure 4: License Terms
This step will install the setup support files. Press “Install” button. See the figure below.
Figure 5: Setup Support Files
Figure 6: Setup Support Rules Progress
This step will check the potential problems that can occur during the installation. All test should be passed in-order to continue to next steps. Incase all the tests passed “Next” button will get activated, press “Next” button. See the screen below.
Figure 7: Setup Support Rules
Select first option “SQL Server Feature Installation” then press “Next” button. See the following screen.
Figure 8: Setup Role
This step offers you to select features of SQL Server that you want to install. Select all the features by pressing “Select All” button and then press “Next” button. See the screen below.
Figure 9: Feature Selection
If all the tests gets passed the press “Next” button. See the screen below.
Figure 10: Installation Rules
In this step we specify instance related configuration. Select “Default instance” option and press “Next” button. See the screen below.
Figure 11: Instance Configuration
This step checks space availability to install the SQL Server. In case of success press “Next” button.
Figure 12: Disk Space Requirement
This step is important in the installation of SQL Server. Press “Use the same account for all SQL Server services”.
Figure 13: Server Configuration
A screen will appear, it will ask about Account Name and Password to be used for services. Browse
“NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE” and press “OK” without entering any password. See the screen below.
Figure 14: Account Credentials
After above step press “Next” button. See the screen below.
Figure 15: Server Configuration Final Step
This is most important step during the installation of SQL Server. This steps asks about the accounts permissions and security mode of Database Engine.
a- Select “Account Provisioning” tab.
b- In “Authentication Mode”, select “Mixed Mode (SQL Server authentication and Windows authentication)”.
c- Specify the password for the SQL Server system administrator (sa) account. Enter password “Password?”
d- Specify SQL Server Administrators, press “Add Current User” button.
e- Press “Next” button after entering all the above information.
See the screen explaining all the above step below.
Figure 16: Database Engine Configuration
Select “Account Provisioning” tab. Add the current user by pressing “Add Current User” button then press “Next” button. See the screen below.
Figure 17: Analysis Services Configuration
This step specify the reporting services configuration. Select third option “Install, but do not configure the report server” and press “Next” button. See the screen below.
Figure 18: Reporting Services Configuration
Select check box and press “Next” button. See the screen below.
Figure 19: Error Reporting
If all the test gets passed then press “Next” button. See the screen below.
Figure 20: Installation Configuration Rules
At this step SQL Server setup is ready for final installation. It will show the summary of all the features going to be installed. Press “Install” button. See the screen below.
Figure 21: Ready to Install
This step shows installation progress. Installation will take about half an hour. Installation times basically depends upon the speed of your system. See the screen below.
Figure 22: Installation Progress
On the completion of installation, it will prompt and show the following screen. Press “Close” button.
Figure 23: Installation Complete
On pressing the “Close” button, setup will ask you to restart your computer in order to take changes. Press “OK” button. See the following screen.
Figure 24: Restart Computer
After restarting your system you can use your MS SQL Server successfully.
/*******************End of Document*******************/